New Release! Git-backed Machine Learning Model Registry for all your model management needs.
Preventing Stale Models in Production
Every model that gets deployed to production experiences some type of drift as the data on production starts to differ from the data the model was trained on. That's why we're going to look at how you can prevent stale models from remaining in production.
Preventing Stale Models in Production
This post hasn't been updated since its release and some of the technical examples may be outdated. Nonetheless, the concepts described still hold true and you should be able to follow along with minor changes.
What happens when the model you've worked so hard to get to production becomes stale? Machine learning engineers and data scientists face this problem all the time. You usually have to figure out where the data drift started so you can determine what input data has changed. Then you need to retrain the model with this new dataset.
Retraining could involve a number of experiments across multiple datasets, and it would be helpful to be able to keep track of all of them. In this tutorial, we'll walk through how using DVC can help you keep track of those experiments and how this will speed up the time it takes to get new models out to production, preventing stale ones from lingering too long.
Setting up the project
We'll be working with a project from Evidently.ai that demonstrates what it would be like to work with a production model that experiences data drift over time. We'll take this to the next level by adding some automation with a DVC pipeline and share the results with others using DVC Studio.
So we'll start by cloning this repo for the project. This project is based on the one created by evidently.ai with some modifications to work with DVC and different datasets.
The reason we're adding DVC and Studio to this project is to automate the way our model evaluation pipeline runs and to version our data as we get new data. We'll be able to share and review the results for each experiment run we do. One of the big problems in machine learning is collaboration, so making it easier to share models, data, and results can save your team a lot of time and frustration.
Set up data drift reports
When the data in production starts to look different from the data that your model was trained, this is called data drift. There are a number of tools that help monitor for data drift like evidently.ai or Aporia.
Since we're working with Evidently.ai, you can see target drift report when you run the notebook for the initial project they made. Here's what it looks like.
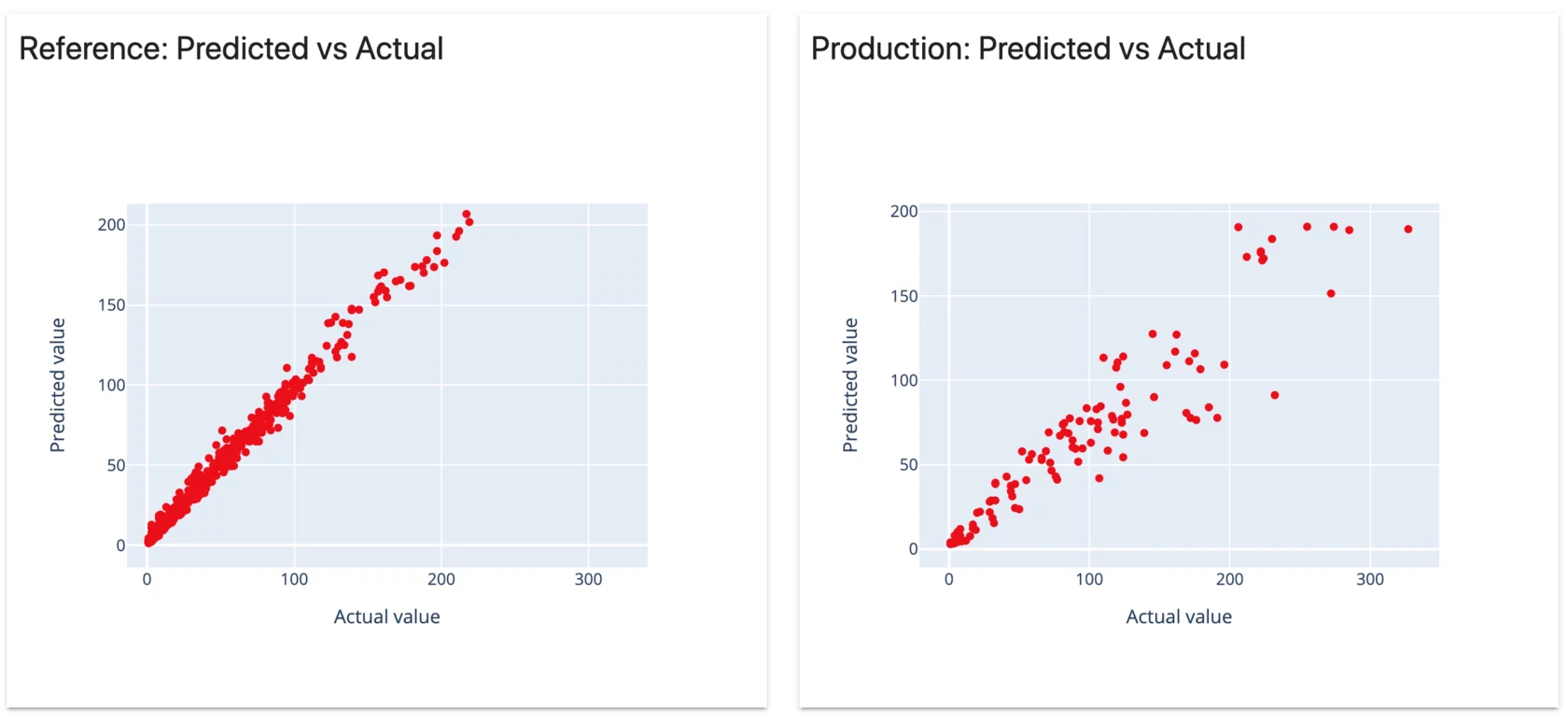
So we see at the end of Week 3 the model is in pretty bad shape. This is where we can bring in DVC to help us get this stale model off of production faster.
Running a training experiment to get production up to date
We'll start by taking a year's worth of data and creating a new model. This might give us a more accurate model to push to production than using weekly data. So we'll take all the data from 2011 (because that's the dataset we have to work with) and make our training and testing datasets. Then we'll check this data into DVC, so it can version it with the following commands:
$ dvc add data/train.pkl data/test.pkl
$ git add data/.gitignore data/train.pkl.dvc data/test.pkl.dvcWe add the .dvc files to Git to ensure that we are only checking in the
metadata for the datasets and not the entire dataset files. Now we can run the
entire MLOps pipeline with
this command:
$ dvc exp runThis will execute the commands we've defined in dvc.yaml and it will give us
the metrics to evaluate how good the model is. Let's take a look at the metrics
so far with the following command:
$ dvc exp show --no-timestamp┏━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━┳━━━━�━━━━━━┳━━━━━━━━━┳━━━━━━━━━━━━┳━━━━━━━━━━━━━┳━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━┓
┃ Experiment ┃ avg_prec ┃ roc_auc ┃ train.seed ┃ train.n_est ┃ train.min_split ┃
┡━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━╇━━━━━━━━━━╇━━━━━━━━━╇━━━━━━━━━━━━╇━━━━━━━━━━━━━╇━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━┩
│ workspace │ 0.70164 │ 0.51384 │ 20210428 │ 450 │ 64 │
│ main │ 0.60791 │ 0.45758 │ 20210428 │ 375 │ 64 │
│ └── 801fdff [exp-a80c0] │ 0.70164 │ 0.51384 │ 20210428 │ 450 │ 64 │
└─────────────────────────┴──��────────┴─────────┴────────────┴─────────────┴─────────────────┘This model doesn't have the best metrics, so we can run more experiments to see
if tuning hyperparameters will help before we deploy this model to production.
Let's change the values of the train.n_est and train.n_est hyperparameters.
We'll
run several experiments
with different values and it will produce a table similar to this:
┏━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━┳━━━━━━━━━━┳━━━━━━━━━┳━━━━━━━━━━━━┳━━━━━━━━━━━━━┳━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━┓
┃ Experiment ┃ avg_prec ┃ roc_auc ┃ train.seed ┃ train.n_est ┃ train.min_split ┃
┡━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━╇━━━━━━━━━━╇━━━━━━━━━╇━━━━━━━━━━━━╇━━━━━━━━━━━━━╇━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━┩
│ workspace │ 0.43501 │ 0.79082 │ 20210428 │ 475 │ 28 │
│ main │ 0.60791 │ 0.45758 │ 20210428 │ 375 │ 64 │
│ ├── 78d29aa [exp-f06bb] │ 0.43501 │ 0.79082 │ 20210428 │ 475 │ 28 │
│ ├── 8fb41cf [exp-1323d] │ 0.42796 │ 0.80841 │ 20210428 │ 425 │ 28 │
│ ├── 434a82f [exp-63459] │ 0.36044 │ 0.87037 │ 20210428 │ 350 │ 28 │
│ ├── 549586e [exp-ceb6d] │ 0.61998 │ 0.4306 │ 20210428 │ 350 │ 64 │
│ ├── fbf8760 [exp-affe2] │ 0.68824 │ 0.50067 │ 20210428 │ 425 │ 64 │
│ ├── 732ab92 [exp-f8e8d] │ 0.65138 │ 0.49431 │ 20210428 │ 500 │ 64 │
│ └── 801fdff [exp-a80c0] │ 0.70164 │ 0.51384 │ 20210428 │ 450 │ 64 │
└─────────────────────────┴──────────┴─────────┴────────────┴─────────────┴─────────────────┘We've run a few experiments with a different hyperparameter value each time and
it looks like exp-63459 is the best one out of them based on both average
precision and the ROC-AUC value. So we'll apply this experiment to our workspace
and choose this model as the one that will go to production. To apply the
experiment, we'll run the following command:
$ dvc exp apply exp-c85c3This will update the workspace with the exact code, data, and hyperparameters that were used in that particular experiment. So we can commit these changes to Git and we'll have a reference to everything we need for this exact model. Now let's say we have deployed this to production and it's been a great model for almost another year, then we start noticing data drift again.
Running more training experiments with new data
That means it's time to update our dataset with the latest data from production and that will include all the data on bike sharing in 2012 (because this is the newer data we have to train with). DVC will note the changes in the data and create a new version record for the updated data automatically.
Next we'll run a new experiment in the project with the following command:
$ dvc exp runThen we can take a look at the metrics with the following command:
$ dvc exp showSince we cleared our workspace by pushing the changes to Git, we'll have a fresh table to look at. Now you should see a table similar to this:
┏━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━┳━━━━━━━━━━┳━━━━━━━━━┳━━━━━━━━━━━━┳━━━━━━━━━━━━━┳━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━┓
┃ Experiment ┃ avg_prec ┃ roc_auc ┃ train.seed ┃ train.n_est ┃ train.min_split ┃
┡━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━╇━━━━━━━━━━╇━━━━━━━━━╇━━━━━━━━━━━━╇━━━━━━━━━━━━━╇━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━┩
│ workspace │ 0.42526 │ 0.82722 │ 20210428 │ 400 │ 28 │
│ main │ 0.69744 │ 0.63056 │ 20210428 │ 475 │ 32 │
│ ├── e76a89d [exp-7d207] │ 0.42526 │ 0.82722 │ 20210428 │ 400 │ 28 │
│ ├── 2a6d647 [exp-7526d] │ 0.74411 │ 0.65808 │ 20210428 │ 400 │ 32 │
│ ├── 467fd3d [exp-dfabd] │ 0.71431 │ 0.6267 │ 20210428 │ 450 │ 32 │
│ ├── 2a2171c [exp-45493] │ 0.58291 │ 0.49201 │ 20210428 │ 350 │ 48 │
│ └── 683dc49 [exp-2649a] │ 0.58421 │ 0.5783 │ 20210428 │ 475 │ 48 │
└─────────────────────────┴──────────┴─────────┴────────────┴─────────────┴─────────────────┘Having the updated dataset made a huge difference in the metrics, and it looks like this model has a different set of hyperparameters that perform well. Now that we have all of the experiments with both the old and new datasets, this is a good time to share the results with your coworkers and get some feedback.
Viewing experiment results in DVC Studio
Because we already have DVC set up in this project, we can run as many experiments as we need to, and it will track which datasets we're working with, the code changes that we make, and it'll let us look at all the results from each experiment in Studio.
If you go to Iterative Studio, you'll be prompted to connect to your GitHub/GitLab account and you'll be able to choose the repo for this project. Once you're connected, you should be able to see all the experiments you've pushed to your Git history.
You can give others on your team access to this, and they'll be able to run new experiments and see the results right in the browser. This is a great tool to use to discuss the next best steps in your model training before you're ready to deploy.
Deploy new model to production
The output of our training stage is the file for the model.pt. Now all we need
to do is get this to our production environment. That could be a web API that
returns results in real-time, or you could do some kind of batch prediction.
Regardless of how you deploy to production, you now have a model that's been
updated to account for the previous data drift.
Conclusion
Now you just have to keep an eye on this new model to make sure that it does stray too far from the results you expect. This is one of the processes you can use to keep your production models from going stale. You could even automate some parts of this process if you know what your thresholds are!